Penile Implant
What is a penile implant (prosthesis)?
A penile implant is a device placed in your penis during surgery to help you get an erection. This device is used for men who have tried other erectile dysfunction (ED) treatments like oral (taken by mouth) medications, urethral suppositories, vacuum devices, or injection therapy that have not helped.
There are two main types of implants:
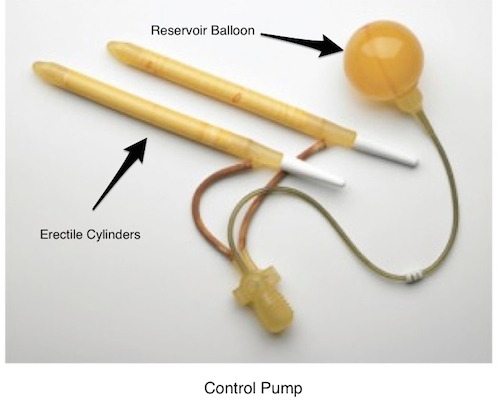
- Inflatable implants: A reservoir (collection) of salt water is placed in your abdomen (belly) and connected to inflatable tubes in your penis. A pump with a release valve is placed in your scrotum. You squeeze the pump to push the fluid into the cylinders to get an erection. Afterward, you release the valve to allow the fluid to go back to the reservoir. When deflated, the penis will be flaccid. This is the most common implant type.
- Semi-rigid rods: This implant stays rigid all the time. It is bent forward for sexual activity or bent up toward the body to hide it when not in use. This article will focus on inflatable implants and not semi-rigid rods. Talk to your urologist for more information.
How is the implant placed?
You will likely be able to go home the same day that you have your penile implant placed. You will be given medication to make you sleep (general anesthesia) or a spinal block that keeps you from feeling pain in the lower part of your body. The surgery usually takes about 45 to 60 minutes. It is done through a small incision (cut) in your scrotum or just above your penis, depending on your case.
If there is bleeding, a small drain will be placed and you may need to stay in the hospital overnight. The drain is removed the next morning. In general:
- A dressing that applies pressure will be placed around your penis and scrotum for 24 hours. Often, this can be removed the day after surgery. The stitches used to close the incision will absorb into your body, meaning they do not need to be removed and will go away on their own.
- Pain after surgery is often mild. You will be sent home with prescriptions for antibiotics, pain medication, and a stool softener.
- It is common to have some scrotal swelling and discomfort after surgery. This often goes away within one to two weeks.
- You should not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds. Avoid exercising and sexual activity for 4 to 6 weeks after surgery.
- You may shower 48 hours after surgery. Do not bathe or submerge your penis in water for one to two weeks after surgery.
- If you have an inflatable implant, you will be taught how to use the pump. You may be given instructions to inflate and deflate the device for 15 minutes twice a day to help stretch the tissues and prevent capsule formation (scarring) around the device.
What are the possible side effects?
Penile implant surgery is usually very safe. Some side effects from the surgery may be:
- Infection.
- Bleeding.
- Implant failure.
- Damage to the urethra (tube where urine leaves your body) that needs to be fixed with surgery.
- Pain, either with the device inflated or deflated.
- In very rare cases, there can be damage to the bowel, bladder, or large blood vessels during the placement of the reservoir balloon.
When should I call my provider?
You should call your provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms after surgery:
- Severe pain.
- Fever. Your provider will tell you at what temperature you should call them.
- Discharge (drainage) or bleeding from the incision.
- Blood in the urine.
- Severe swelling.
What else should I know?
Although the cylinders expand (grow) in length and width, the erection that you get with an implant is often smaller than your natural erection before having erectile dysfunction (ED). The erectile cylinders in some men do not go fully into the tip of the penis. This is a separate area that normally fills with blood in men who do not have ED. If the cylinders do not go far enough into the tip of the penis, the head of the penis may "droop" somewhat with erections. This should not affect sexual activity.
An implant does not change the feeling on the skin of the penis. It does not affect the ability to reach orgasm or ejaculate. If your implant needs to be removed, you will likely need to have it replaced to have erections in the future.