Treatments and Side Effects
What are some treatments of cancer?
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is the use or manipulation of hormones naturalor synthetic to treat disease. For example in prostate cancersome frequently used hormones are Eulexin and Flutamide. Hormonetherapy is used in three ways:
- injection or orally
- surgical removal of hormone producing glands
- radiation treatment to destroy hormone producing cells
Radiation Therapy
This is a picture of the clinic at the University of Pennsylvania Hospital. Patients come here to be examined before receiving radiation therapy. |
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy penetrating rays orsubatomic particles to treat or control cancer. Radiation canbe given in two ways, externally by a special machine, or internally,by placing radioactive substances in the body. External radiationis more commonly used and sometimes both methods are used.
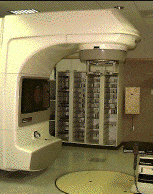
This is a picture of the linear accelerator which is the machine radiation oncologists use to administer radiation treatment. |
- External radiation therapy - a machine delivers radiationto cancer inside the body or on the surface of the skin. Differentmachines are used depending upon the location of the cancer andthe energy of the machine.
This is a picture of the simulator. Radiation oncologists use this machine to map out how they are going to give the radiation treatment. |
- Internal radiation therapy-a radioactive substance is sealedinside a small container such as a wire, tube, seed, capsule,or needle called an implant. The implant is placed directly intothe tumor or into a body cavity. The container remains insideside your body, but the radioactive substance only remains inyour body for the length of its half life. For instance if thematerial that radiation oncologists are using has a half lifeof 72 hours the material only effectively fights the cancer in your body for 72 hours. For some cancer sites it may be permanently implanted. Unsealed radiationin liquid form may also be used.
This is a picture of the dosimetry unit. This is where doctors discuss the amount of radiation they are going to use based on the condition of the patient. |
Palliation
Sometimes cancer patients experience bone pain, SVC(superior vena cava) syndrome, or other symptoms that may or may not becurative. If this happens radiation oncologistsmay prescribe treatment and/or medication to alleviate the symptoms.Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment or control of cancer using anticancer drugs,highly toxic medications that destroy cancer cells by interferingwith their growth or by preventing their reproduction. Often timesthese drugs are combined so that they are more effective in cancertreatment. Some known combinations are cytarabine and doxorubicinor doxorubicin and carmustine. Chemotherapy is also used to prolonglife when a cure is improbable and to relieve symptoms.
Biological Therapy
Biological therapy uses the immune system, either directly orindirectly, to fight cancer or to lessen side effects that maybe caused by some cancer treatment. Biological therapies usedto treat cancer restore the body's natural cancer defense mechanisms,reverse the process that changes a precancerous cell into a cancerouscell, and prevent cancer cells from spreading to other parts ofthe body.
Surgical Therapy
Surgical removal of cancerous tumors is divided into several typeseach serving their own individual purpose. They are as follows:
- Staging surgery
Staging surgery is performed to determine the extent of disease.Based on the findings after this surgery, the oncologists selectsthe procedure that would be most appropriate for this stage ofthe disease. Staging is also used to eliminate radical proceduressuch as hysterectomies, and prostatectomies.
- Definitive surgery
Definitive surgery tries to remove as much of the tumor as possible.During this procedure the entire tumor as well as surroundingtissue are removed to try to prevent metastases. If done in theearly stages, this surgery can cure some cancers.
- Preventive surgery
Usually for patients with family history of cancer, or increasedrisk of developing cancer, tissue where tumor is thought willdevelop is removed.
- Palliative surgery
Palliative surgery relieves symptoms in advanced stages of cancerwhen medication does not work. Some procedures involved surgicalinterruption of nerve pathways due to pain.
Side Effects
Besides the removal of the cancerous tumors many of the therapieshave side effects. Some are nausea, constipation, diarrhea, hairloss, and vomiting. As a result, doctors have developed ways toalleviate some of these side effects either through medicationor by following these simple steps:
- nausea and vomiting (most frequently linked to chemotherapyas well as radiation to the stomach or brain)
-eat slowly and chew well
-eat dry foods like toast, dry cereal, and crackers
-drink clear unsweetened beverages
-breathe through mouth when feeling nausea
- diarrhea (most frequently linked to radiation to the colon,rectum, or prostate)
-try a clear liquid diet to give bowels a rest
-drink fluids to replace those lost
-eat smaller amounts of food more often
-avoid highly spiced foods a sweets
-avoid milk and milk products
- constipation
-drink a lot of fluid
-eat high fiber foods
-keep up normal level of activity; exercise if possible
Sometimes the side effects are handled surgically such as thereformation of breast after a mastectomy or the reconstructionof a patient's face after face or neck treatment.