Head and Neck Cancer: The Basics
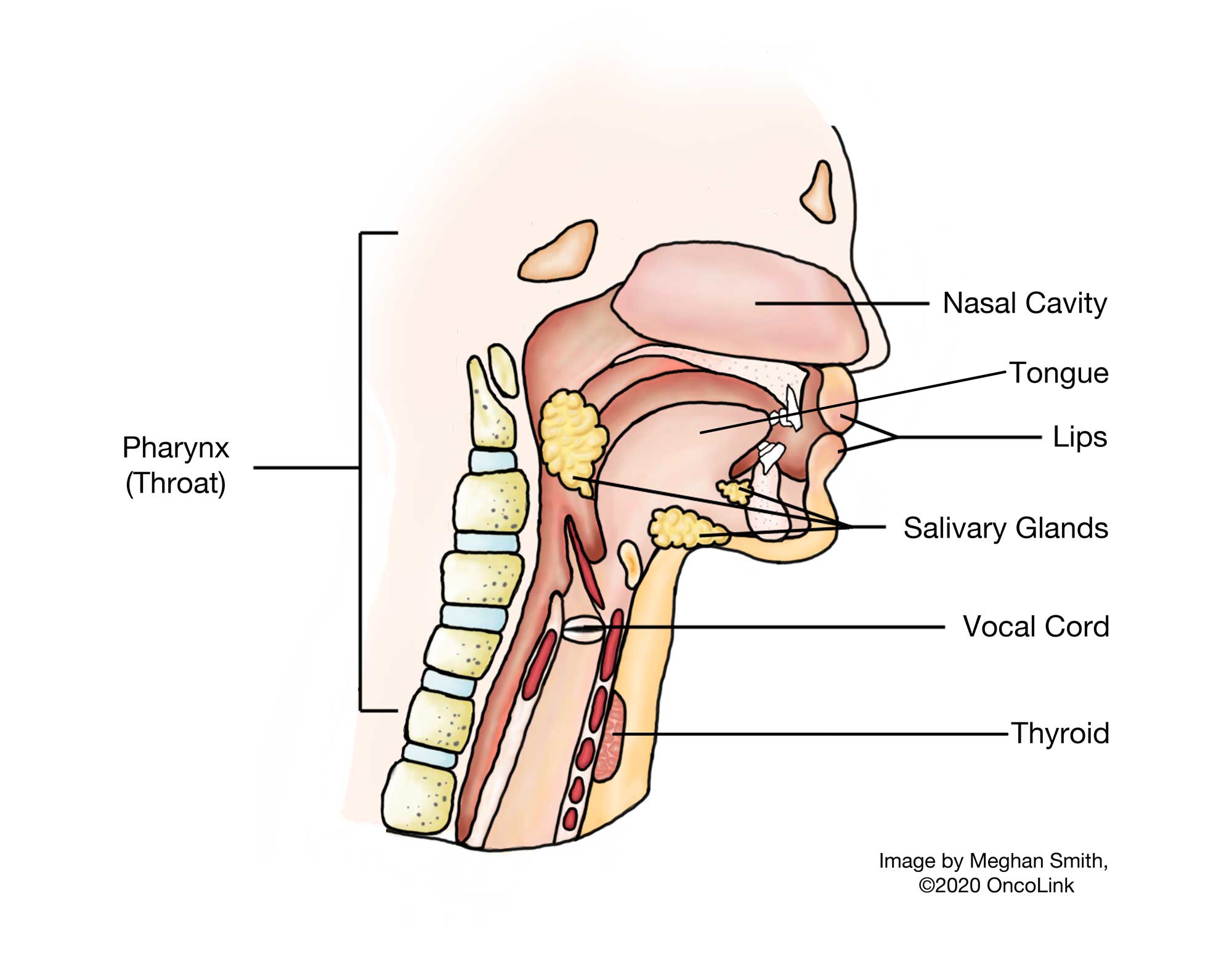
Head and neck cancer is caused by cells growing out of control. As the number of cells grows, they form a tumor. The head and neck are made up of many different areas, and cancers are grouped by the area they are in:
- Oral cavity: Includes the lips, front part of the tongue, roof and floor of the mouth, parts of the gum line, and the inside lining of the cheeks.
- Nasopharynx: The areas of the pharynx (throat) behind the nose and the lining of the nose.
- The sinuses: Hollow spaces in the bones of the head and the nasal cavity (open space inside the nose).
- Salivary glands: Found in the bottom of the mouth and produce saliva.
- Oropharynx: Area of the pharynx (throat) behind the mouth, the soft part of the roof of the mouth, tonsils, and the base of the tongue.
- Hypopharynx: The area of the pharynx (throat) below the oropharynx down to the esophagus (the tube that food goes down).
- Larynx: The voice box and the epiglottis, which are in front of the hypopharynx.
- Parts of the ear: The external auditory canal, middle and inner ear.
To see more images of head and neck cancer anatomy, click here.
Head and neck cancer that has spread from one part of the head and neck to any other part of the body is called metastatic cancer.
Risk Factors
Head and neck cancers are often caused by tobacco and alcohol use. Both smoked and smokeless types of tobacco can raise your risk. Other risk factors are:
- Infection with some strains of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV).
- Having a diet high in salt-cured foods.
- Long-term sun exposure to the lips.
- Exposure to substances like asbestos, second-hand smoke, radiation, and wood dust.
- Inactive infection with the Epstein Barr virus.
- Poor dental/oral health.
Screening
There are no screening tests to find head and neck cancers early. Your dentist should check your mouth, tongue, and neck during dental exams.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of head and neck cancer depend on where the tumor is. Symptoms can be:
- Weight loss from trouble swallowing food.
- A new lump or sore that doesn’t go away.
- Sore throat.
- Change in voice.
- Pain.
Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer
If your healthcare provider thinks you may have head and neck cancer, you will need tests done to look at the inside and the outside of your head and neck. Tests may be:
- Endoscopy uses an endoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera on it. It is put into your nose or down your throat to look at and biopsy any concerning areas.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
- PET scan.
Staging for Head and Neck Cancer
To guide treatment, head and neck cancer is given a stage. The stage is based on:
- Where and how big the tumor is.
- If cancer cells are in the lymph nodes.
- If cancer cells are in other areas of the body.
Stages range from stage I (one) to stage IV (four). Stage I are the smallest, most confined tumors and stage IV are tumors that have spread to other areas of the body, also called metastatic cancer. The stage and type of cancer will guide your treatment plan.
Treatment
Head and neck cancers are treated in different ways based on where the tumor is, the stage of the tumor, and how healthy the patient is. In general, these treatments may be used:
- Surgery: The goal is to remove the whole tumor and some healthy tissue around it. You may need reconstructive surgery to save function (how the area works) and appearance (how the area looks).
- Radiation: Uses high-energy x-rays to destroy cancer cells. It can be used before or after surgery and/or chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: The use of medication to kill cancer cells. It may be given with radiation to help the radiation work better, this is called radiosensitization.
- Targeted therapy and Immunotherapies (another type of medication): Can be used in squamous cell head and neck cancers.
This article is a basic guide to head and neck cancer. You can learn more about your type of head and neck cancer and treatment by using the links below:
Treatment Options for Head and Neck Cancers
Side Effect Management and Support Resources
Hypopharyngeal (Lower Throat) Cancer: Staging and Treatment
Laryngeal Cancer: Staging and Treatment
Nasal Cavity (Nose) and Paranasal Sinus Cancers: Staging and Treatment
Nasopharyngeal (Upper Throat) Cancer: Staging and Treatment
Oral Cavity (Mouth), Lip, and Oropharyngeal (Throat): Staging and Treatment